Do you know that the birth of an operational excellence strategy took place in a manufacturing environment? During the revolutionary period, its objective was to meet regulatory requirements and mitigate risks from catastrophic failures.
But users realized its broader application as a tool to improve manufacturing processes and practices.
Today, best-in-class manufacturing companies are using it as a management system to achieve sweeping and breakthrough improvements in innovation, profitability, technology, efficiency, revenue growth, customer satisfaction, and other focus areas of the business.
In my opinion, there is a strong need for a robust strategy formulation process, and the outcome of this process should be strategic goals and action plans that will lay the foundation for the transformation process.
That is why I have written this article that will explain everything related to operational excellence strategy and its role in today’s competitive environment.
Competitive Strategies For Market Leadership
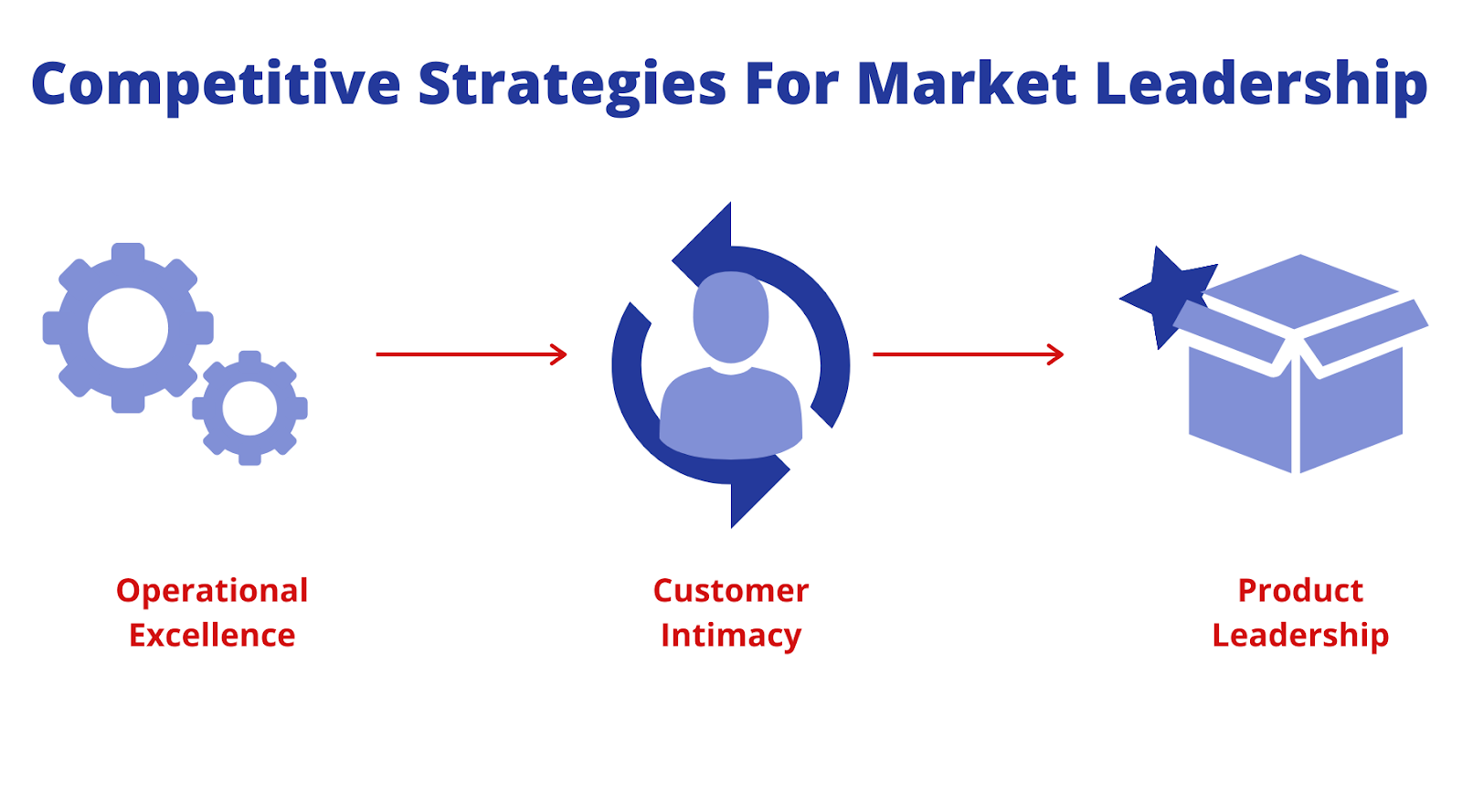
To survive in the marketplace, companies must opt for a competitive strategy.
Authors Michael Treacy and Fred Wiersma explained three competitive strategies: operational excellence, customer intimacy, and product leadership.
They have described in their book, The Discipline of Market Leaders (1997). The author’s main conclusion was that companies must choose and achieve market leadership in one of the three disciplines.
Also, they should perform to an appropriate level within the other two.
What is Operational Excellence?
There is no universal definition of operational excellence; this is because organizations differ in vision, mission, strategic goals, and focus areas.
As there is a diversity in definitions, there is one common theme among most of them. This is to strive for dramatic improvements to sustain competitive advantage.
According to Institute for Operational Excellence–
“To leverage operations to attain business growth, the primary step is to know what Operational Excellence is, and so how we achieve it. Think of it as answering the question: Where will this journey of improvement take us? A good answer is that this journey will take us to the purpose at which every employee can see the flow useful to the customer, or operational excellence, and fix that flow before it breaks down.”
Let’s have a look at Kevin Duggan, Founder of the Institute for Operational Excellence gives us his best definition of Operational Excellence & Operational Excellence Strategy.
So, Operational excellence is a framework to focus on growth and execute its strategy better than its competitors.
Also, companies trailing Operational Excellence do two things differently. Firstly, they manage their business and operational processes systematically and invest in developing the proper culture.
The goal is to build a single, integrated enterprise-level management system. This system should focus on guiding principles of integrity, questioning attitude, always problem-solving, daily continuous improvement mindset, level of knowledge, teamwork, and process-driven.
Additionally, operational Excellence can also be viewed as execution excellence.
Some of the key process methodologies used are Lean Manufacturing, Six Sigma, Kaizen, Hoshin Planning, Balanced Scorecard, etc that I have discussed below in the article.
Examples of companies with this competitive strategy include Wal-Mart, IKEA, Southwest Airlines, McDonald’s, and FedEx.
Customer Intimacy
The customer intimacy strategy focuses on offering a novel range of customer services that enable the personalization of services and so, the customization of products to satisfy different customer needs.
Often companies who adopt this strategy pack their services and products into a “solution” designed specifically for the individual customer.
The successful design of solutions requires vendors to possess deep customer knowledge additionally as insights into their customers’ business processes.
These solutions provide the most affordable option for the customer that is the most innovative and is considered to be “good enough.”
So, true customer affinity is achieved by aligning product development, manufacturing, administrative functions, and executive focus on the needs of the individual customer.
Customer-centric companies tend to possess a decentralized organization that allows them to find out and alter quickly in line with customers’ needs.
These sorts of companies often keep the whole ecosystem of partners for the production and delivery of services and products to their customers.
Examples of companies that pursue this kind of strategy include IBM, Amazon.com, Lexus, and Virgin Atlantic.
Product Leadership
Product leadership is a competitive strategy that aims to create a culture of bringing superior products to promote. So, product leaders achieve premium market prices because of the experience they create for the customers.
The corporate disciplines they cultivate include:
- Research portfolio management
- Teamwork
- Product management
- Marketing
- Talent management
Also, product leaders recognize that excellence in creativity, problem-solving, and teamwork is critical to their success.
This implies that product leaders seek to leverage their expertise across organizational and geographical boundaries by mastering such disciplines as knowledge and collaboration management.
The consumer electronics, automotive, fund management and pharmaceutical industries include many companies that are using product leadership. Examples of these include Fidelity Investments, Apple, BMW, and Pfizer.
Benefits of Operational Excellence Strategy
Operational excellence yields tangible results. A company that attains operational excellence will have higher revenues, lower costs, less risk, and more satisfied customers than a competitor that doesn’t.
Here are a number of the commonly cited benefits of operational excellence:
- Efficiency in processes and use of resources
- Cost reduction or containment
- An engaged, stable workforce
- Cohesive management
- Strong shareholder value
- High-quality standards
- Beneficial partnerships with suppliers
Operational Excellence Roles and Responsibilities
The improvement in the team that is involved in operational excellence will vary in number based on the size of your organization.
Still, this group should have a minimum of some members like an expert within the subject. Typical roles include a director of operational excellence who is liable for developing and executing improvement initiatives.
Other members could be your staff with experience in facilitating Lean management and implementing related projects. The goal is to form operational excellence, a core strength of the corporate.
Also, staff with training and certifications such as Six Sigma will lead the effort and may include master black belts and black belts.
The operational excellence group’s responsibilities will include duties like participating in cross-functional project teams and overseeing process improvement events.
In addition, this will also include defining and monitoring performance metrics, fostering culture, and mentoring frontline operational excellence leaders.
Operational Excellence Goals
You should first, define what you want your operational excellence initiative to achieve. Setting goals will help you to measure success.
Therefore, you can specify operational excellence goals in four categories as finances, operations, culture, and enterprise. Let’s check out some specific examples in each category.
Examples of Financial Operational Excellence Goals:
- Higher sales
- Capacity utilization
- Cost control or reduction
- Stronger cash flow
- Greater asset productivity
- Higher capital efficiency
- Shorter payment cycles
- Reduced receivables
- Efficiencies in supply chain
Examples of Operational Excellence Goals for Operations
- Decreased accident rates or time lost to injuries
- Improvement in defect or error rates
- Fewer regulatory or compliance issues
- Higher customer satisfaction
- Less waste in the value stream
- Smaller environmental footprint
- Reduced downtime
- Greater customer retention
- Higher output or productivity
Examples of Operational Excellence Goals for Culture
- Increased number of employees and provide training with key skills
- Greater employee engagement
- Enhanced accountability by individual team members
- Improvement in cross-department cooperation
- Higher employee satisfaction scores
Examples of Operational Excellence Goals for the Enterprise
- Closing the gap between the current state and optimal performance
- Realizing the financial value of that gap
- Achieving a level of operational excellence maturity parallel to the industry standards.
Operational Excellence Methodologies
Lean Manufacturing
Lean Manufacturing is about eliminating waste from the manufacturing process without negatively impacting productivity.
In other words, it aims to implement business processes that achieve high quality, safety, and worker morale and reduce cost as well as shortening lead times at the same time.
Furthermore, waste is any activity or expenditure of resources that does not add value from the customer’s point of view. In Lean manufacturing, there are seven types of waste as mentioned:
- Overproduction against plan
- Waiting time of operators and machines
- Unnecessary transportation
- Waste in the process itself
- Excess stock of material and components
- Non-value-adding motion
- Defects in quality
Six Sigma
Six Sigma is a set of tools and techniques for the improvement of business processes. The goal is to create customer experience improvement using variation identification and elimination.
This can be accomplished by implementing DMAIC, a Six Sigma sub-methodology. DMAIC is the abbreviation for:
Define: define the problem to solve it.
Measure: Take a more detailed look into your processes and measure all of your available data as well.
Analysis: Perform an analysis of your findings and figure out the problem’s root.
Improvement: Once you analyze your data, find possible solutions and implement them.
Control: Ensure to maintain your newly implemented process.
Kaizen
Kaizen is Japanese and stands for “Continuous Improvement“. It refers to activities aiming for the implementation of positive, ongoing changes at the workstation.
In other words, it is a strategy that involves all employees from every company level to work together and proactively to achieve regular, incremental improvements to the manufacturing process.
Kaizen emphasizes the significance of continuous improvement. It is not enough to undertake changes once.
Organizations have to make an effort in continuing improvements repeatedly. Therefore, various companies have applied Kaizen’s concept and strategy to reduce costs, increase employee productivity, and improve the overall customer experience.
Strategic Operational Excellence Model
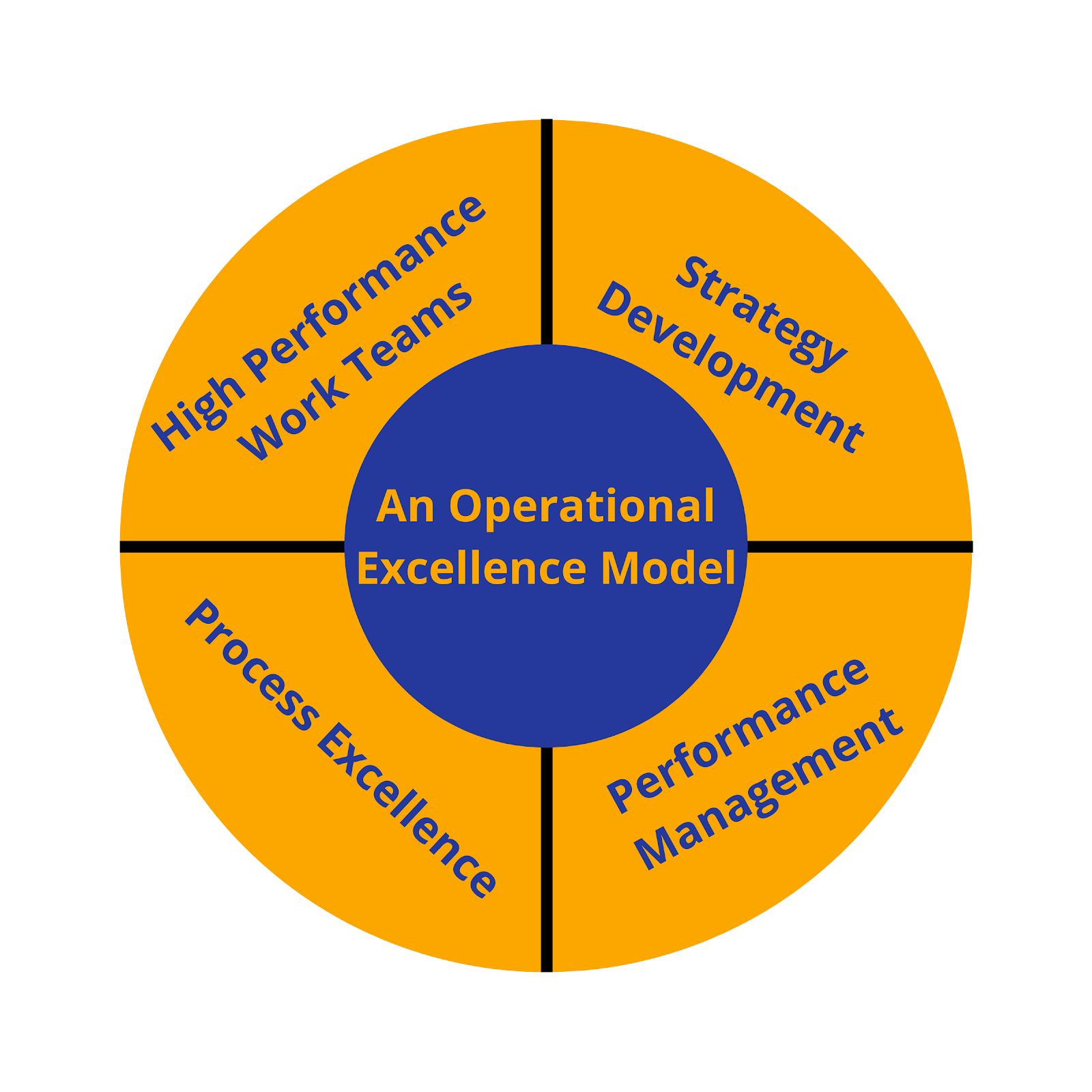
The operational Excellence strategic model is based on four building blocks: Strategy Deployment, Performance Management, Process Excellence, and High-Performance Work Teams.
Strategy Development
A strategy is an expression of what a company intends to do to induce from a current state to a future state.
Strategic plans are often developed in isolation and barely aligned across the organization.
As a result, the organization’s strategy and strategic objectives aren’t well defined, not well communicated, and don’t impact day-to-day higher cognitive processes and resource allocation.
Lack of strategy is a serious problem that can result in ad hoc improvements that don’t contribute to the organization’s overall needs.
“In the global and competitive environment of today and tomorrow, organizations must rethink and reshape their approach to execution in order to stay competitive. Operational excellence & Lean Six Sigma is the strategic initiative under which this process can take shape.“
Performance Management With Balanced Scorecards
In 1990, Art Schneiderman participated in a research study by David P. Norton and Robert S. Kaplan, and during this study introduced his work on Balanced Scorecards.
Subsequently, Norton and Kaplan included anonymous details of Balanced Scorecard in their 1992 article “The Balanced Scorecard – Measures That Drive Performance”, Harvard Business Review, February 1992.
While traditional goal-setting often focuses on financial, and thus lagging, measures, the Balanced Scorecard approach broadens the scope of indicators to incorporate leading performance indicators from the subsequent four key areas or perspectives.
Financial
- How do you want to look to your shareholders?
- Indicators specialize in whether your strategic and operational plan contributes to your top-line, bottom-line, and/or market share.
Customer
- How do you want to look to your Customers?
- Indicators focus on the specific measures that matter the most to your Customers.
Internal Business Processes
- At what capabilities and internal processes do you want to excel?
- Indicators specialize in internal operations that enable Customer satisfaction, growth, and profitability.
Learning and Growth
What skills and competencies do you ought to implement in your strategic and operational plan?
Indicators specialize in your organization’s ability to innovate, improve, and execute.
The Balanced Scorecard approach not only monitors present performance (lagging indicators) but also leading indicators about how well the organization is positioned to perform and compete well in the future.
“Balanced Scorecards tell you the knowledge, skills, and systems that your employees will need (learning and growth) to innovate and build the right strategic capabilities and efficiencies (internal processes) that deliver specific value to the market (customer) which will eventually lead to higher shareholder value (financial).”
– Robert Kaplan & David Norton
Process Excellence
Operational Excellence organizations are process-centered organizations that have simple, efficient, and effective management, value creation, and support processes to deliver best-in-class products and services consistently.
Process Excellence methods and tools, including Lean Management, Six Sigma Methodology, and also the 8D Problem Solving Process, are core competencies.
Therefore, operational Excellence organizations utilize them to achieve the organization’s strategic and operational objectives and goals.
Thus, these methodologies will ensure that progress toward the organization’s strategic breakthrough and operational objectives is made.
Also, the risks and roadblocks are identified and countermeasures are implemented promptly.
High-Performance Work Teams
Operational Excellence organizations continuously strive to increase the engagement, education, and empowerment of their employees through strong values, guiding principles, leadership development, coaching, and continuous competence development.
You can also get in touch with Gary Keating from Action Coach Bristol.
Principles of Operational Excellence
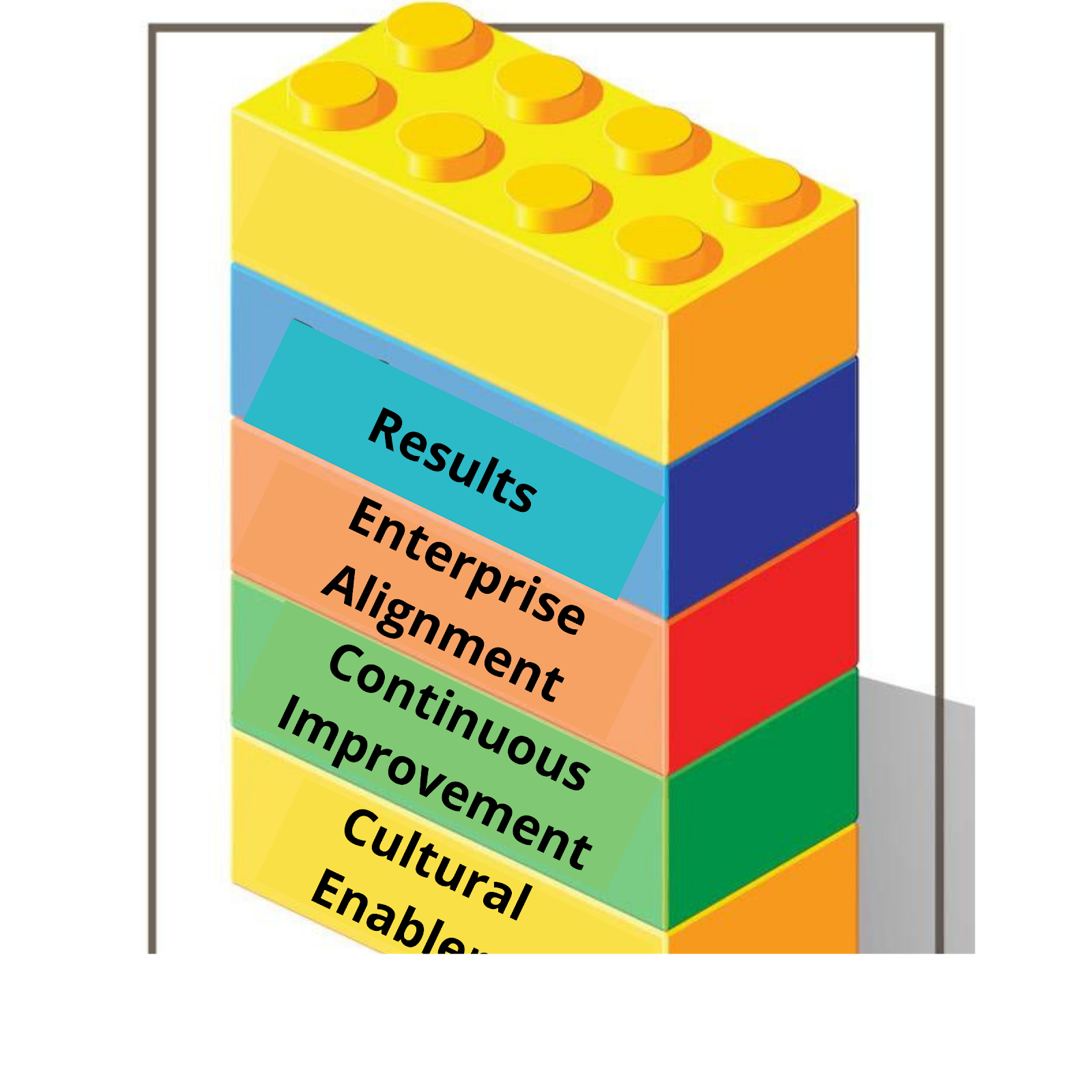
Shingo’s ideas and 18 books were hugely influential in the West, and, in 1988, Utah State University’s Jon M. Huntsman School of Business created the Shingo Prize for Operational Excellence to acknowledge companies that excel in applying Shingo’s principles
These principles are grouped into four areas that build on one another like a pyramid:
-
At the Base Are Cultural Enablers:
- Respect every individual.
- Lead with humility.
-
Next Are Drivers of Continuous Improvement:
- Seek Perfection.
- Assure Quality at the Source: Do work right the first time and correct mistakes when they occur.
- Flow and Pull Value: Maximize customer value by creating an uninterrupted, continuous production flow that responds to true customer demand.
- Embrace Scientific Thinking: Follow a disciplined process of problem-solving through experimentation and learning, and encourage employees to evaluate new ideas without fear of failure.
- Focus on Process: Do you know many organizations blame failure on individuals. But, you need strong processes to produce consistently good results.
-
Moving Toward the Top of the Pyramid Are Factors That Create Alignment Across your organization:
- Think Systemically: Break down silos and think of your organization holistically. Recognize that processes and people are interconnected and work to break down barriers.
- Create Constancy of Purpose: Be clear about your mission, strategy, and plans, and tie your daily activities to your larger purpose and goals.
-
At the Peak of the Pyramid Lie Results:
- Create Value for the Customer: This is your raison d’etre, so you must constantly strive to know what your customers need and expect.
Path Towards Operational Excellence
Introduce Employees to Operational Excellence
It is essential to introduce the concept in a way that emphasizes the desire to provide the ultimate value to the customer, with the most efficient use of resources along the way.
Employees should understand the guiding principles and be recognized and rewarded when they see the world through that lens.
So, the tools that you simply will use to attain operational excellence are important but start with the concept itself.
Reduce Top-Down Thinking
Traditional companies work in a strict top-down approach with all directions coming from the top.
Operational excellence requires a different approach in which front-line employees are empowered to recognize and respond to interruptions in the flow of value.
Ideally, the upper levels of the hierarchy exist to manage the strategic direction of the organization and to provide the resources that employees need to be successful in a constant feedback loop.
Visualize Flow
Although the overarching objective of operational excellence is to create an unhindered flow of value to the customer, another of its primary concerns is transparency.
So, if you can see roadblocks, process irregularities, resources that aren’t at capacity, and poorly aligned goals you can do something about them.
That’s why many improvement tools are built in a way to allow visual management. So, people process images much more quickly than text, that’s why icons, signs that use color and shape, and dashboards are so popular.
Introduce Standard Work for Normal and Abnormal Flow
Without a standard, there can be no improvement. We mentioned the importance of scientific thinking.
A standard is a control group for your improvement experiments. In most cases, processes will run normally, and therefore the usual standard is often applied.
Also, there should be standard work for when processes become out of control so that the people on the front lines know exactly what they should do.
Align Objectives and Accountability
The most successful companies have a clear set of business objectives.
Part of strategy deployment is ensuring that each individual knows how they can best contribute to achieving the most important goals. Hence, performance evaluation relies partly on engagement with improvement work.
Set up the Framework for Collaboration and Improvement
Having a structure to your improvement work is important.
In other words, your improvement platform should provide a central repository for all opportunities for improvement, allow for cross-functional collaboration, and offer active alerts and notifications to make sure that progress never stalls.
So, the technology will function as a knowledge bank for the organization so that no lessons learned are ever lost.
Implementation of Operational Excellence in Various Sectors
Manufacturing
Companies like Toyota and Ford had the greatest impact on operational excellence. Lean is a common approach to operational excellence in manufacturing.
Moreover, the Institute for Operational Excellence emphasizes the importance of creating flow visually, meaning that you simply provide visible signals and indicators for the timing of production.
A red light that illuminates when a machine is jammed or a Kanban card that signals it is time to replenish raw materials makes the state of the value stream instantly apparent.
So, employing this method increases efficiency by connecting processes and, thereby, enhancing flow within the value stream.
Information Technology
Information technology organizations that are operationally excellent focus on continuously improving their processes and their culture.
Moreover, the Agile and Scrum methodologies are natural complements to the operational excellence of these IT firms.
So, at these companies, the operational excellence approach translates into ensuring they need employees with versatile skills.
Healthcare
Efforts at hospitals and other health institutions focus on improving processes to use resources more efficiently, eliminating mistakes and unnecessary procedures, and improving health outcomes.
For example, a Johns Hopkins University program gave doctors and nurses a five-step safety checklist to follow when they place central-line catheters in intensive care unit patients.
In other words, the program also helped promote a culture of safety, empowering all caregivers to speak up if employees do not follow safety rules.
Marketing
For marketing teams, operational excellence often emphasizes the worth of the customer and systems. The customer may be an internal or external stakeholder, but it is still the customer who determines value.
Also, the adoption of data-driven management, tracking the performance of marketing efforts, establishing benchmarks, evaluating effectiveness, and tying this performance to business outcomes enables marketers to identify process improvements.
Possible Challenges Faced
Research by McKinsey & Company finds that more than 70 % of organizational transformations such as operational excellence fail. Its common causes are flawed leadership and poor communication.
McKinsey finds, your company can beat those odds, by taking a “rigorous, action-oriented approach”. This approach should include effective communication, active leadership, empowered staff, and an environment of continuous improvement.
Also, experts say that the causes for failure usually fall under the headings of leadership, mindset, and execution.
Reasons that leadership causes operational excellence programs to fail are: senior management either lacks understanding or expertise in operational excellence and embarks on the hassle for the incorrect reasons.
Additionally, operational excellence can run aground if the correct mindset isn’t in situ. Resistance to alter among staff can even derail an operational excellence program.
Execution-related reasons for failure include the following: implementing your effort top-down without bottom-up feedback; making too many changes in a short time; confining improvement efforts within silos so the whole organization does not benefit.
Operational Excellence Tools
As you strive for operational excellence, use tools to support this effort, like business process management applications.
Today’s cloud-based software makes it straightforward for organizations of any size to access the resources they need cost-effectively, without accruing technical debt.
One such tool is Smartsheet, an enterprise providing a work execution platform that changes the way teams, leaders, and businesses get work done.
Over 80,000 brands and a lot of information workers trust Smartsheet because the best way to plan, capture, manage, automate, and report on work.
So, you can create automated business processes without complex formulas, a single line of code, or help from IT.
Use Smartsheet to automate and streamline the subsequent processes: timecard tracking, sales discounts, procurement, HR hiring, content, and more.
Also, Smartsheet integrates with the tools you already use to connect your efforts across applications.
Operational Excellence Examples
Sanofi Pasteur
Sanofi Pasteur is the vaccines division of the French multinational pharmaceutical company Sanofi.
It introduced a ‘Big Opportunity’ Project to improve its substandard manufacturing culture. So, the company allowed employees to experiment and find new programs and solutions.
As a result, the company saw massive improvements in quality and culture helping it transform within a short period.
Additionally, it recorded happier employees and a less stressed work environment that pushed everyone to work better.
Philips Lighting
Philips Lighting also saw great results by using Lean Management and Six Sigma methodologies.
So, the company achieved consistent delivery reliability and pulled lead times from 1 percent to 42 percent by improving processes and concentrating on delivering excellence.
IBM
IBM is another company that brought a unique innovation strategy to enhance productivity and reliability.
Therefore, the company automated several repetitive and manual tasks to create employees more productive and increase quality and efficiency.
In addition, these companies improved technology, concentrated on all the processes, improved work culture, and joined hands with reliable partners to identify and improve the abnormal flow of work and achieve excellence.
Conclusion
One important thing to note here is the Operational Excellence journey can only reach their destination if they have a convincing strategic intent, sound strategy, robust action plan, and methodical deployment of plans to the shop-floor level and 5) a method to measure progress.
Reaching one’s destination is certainly an enormous achievement; though in today’s world of rapid changes that demand faster, better, and more cost-competitive products and services.
Therefore, these challenges can be overcome, with leaders “walking the talk” and an organizational culture that is ready to embrace excellence.