To understand private placement examples, let’s first understand that conventional wisdom beseeches investors to balance and diversify. But there are volatility and interest rate yields that do not even keep pace with inflation.
So, conventional wisdom can burn. That is why savvy, high-net-worth investors hedge against these downsides. They do so with a broad range of alternative classes.
These include commodities, real estate, notes, and private placements.
Private placements are investments in private enterprises such as real estate ventures. And while risky, private placements offer investors an array of dynamic opportunities.
They allow portfolio diversification with a low correlation to public markets.
This article will guide you through some real-world examples of private placements. In addition, it will also show why private placements are essential for businesses.
Understanding Private Placement
There are minimal regulatory requirements for a private placement. This is even though, like an IPO, it involves securities sales. The sale does not need the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) registration.
The firm does not have to provide a prospectus to potential investors. Detailed financial information may not be disclosed.
Stock sale on public exchanges is regulated by the Securities Act of 1933. This was enacted after the market crash of 1929. It ensures that investors receive enough disclosure when they buy securities.
Registration exemption for private placement offerings is provided by Regulation D of that act.
The same regulation allows an issuer to sell securities to pre-selected investors. These investors meet the specified requirements of the issuer.
A private placement memorandum (PPM) is used to sell private placements. They cannot be marketed to the general public.
It specifies that only accredited investors may take part. So, these may include entities such as venture capital firms that qualify.
Private Stock Deals
Private stock issues or private offerings are also included in private placement class investments. They are generally offered to institutional investors.
These include large banks, mutual funds, insurance companies, and pension funds. But these investments are also offered to qualified high net worth individuals.
Investors can get in on the ground floor of an enterprise. It has the potential for phenomenal returns.
Private placements can also be a high-value strategy.
They offer firms an infusion of capital far more quickly. Therefore, they are not subject to costly public disclosure obligations like public offerings.
Examples of Private Placements
Private placements range from friends and family investments to angel investments. It can be institutional and venture capital investment in a growth company. Here are some real-world examples of Private Placements:
- You hear about a friend’s startup that raised a small amount, say $200,000, for a stake in their company. It may have been a private placement to one or more high net-worth investors. They are known as angel investors.
- You read about a high-tech company raising $10 or $30 million in what you hear is a “Series A Funding Round.” That is also a private placement, probably to more than one venture capital fund.
- A hedge fund raises $10,000,000 for investment purposes from a couple of institutions. Within 15 days of the sale, they file a Form D with the SEC as this is the third type of private placement.
Goldman Sachs reaches out to Warren Buffet
During the 2008 crisis, all the Investment banks were on the verge of collapse. This was after the fall of Lehman Brothers. This was due to the Subprime Mortgage crisis.
Moreover, Goldman Sachs reached Warren Buffet to offer a 5% stake. Warren buffet got a private placement. Due to the trust that the market had in Warren Buffet, more investors invested in Goldman Sachs, and it was saved.
Goldman Sachs offers shares to Facebook
In 2011, Goldman Sachs offered private shares to Facebook at its IPO. It was offered with a $2 million minimum.
There was a 4 percent placement fee along with 5 percent of gains. That contrasts with the standard private placement fee of 1 to 2 percent.
Facebook’s underwriters settled at an IPO price of $38 per share for a $104 billion market valuation. This was the most massive valuation ever of an American firm at the time.
Today Facebook sells for roughly $78 per share for a market valuation of $203 billion. That private placement turned out to be a hugely lucrative play for those investors.
So, this was true even with the steep fees.
Neuro Research Group got a lucrative private placement
US-based firm Neuro Research Group, or NRG, engaged C.B. Capital Partners. It wanted a private placement.
NRG was a next-generation medical device company. It focused on its core product development and clinical trials’ core operations.
At the same time, C.B. Capital’s investment bankers executed private placement. To do so, C.B. prepared a confidential private placement memorandum.
It got in touch with interested investors and sought letters of intent. It conducted due diligence and evaluated proposals.
Also, it secured ten million dollars worth of aggregated funding for NRG. This was at a favorable per share valuation.
Mars gets an astronomical private placement
Mars, a household name, is a secretive user of the capital markets. It holds the record for the most extensive U.S. private placement.
The confectioner raised about $2.5 billion in a single offering last year.
Why Does Private Placement Matter?
Accredited or sophisticated investors get private placement securities. They involve a specific business activity with specific personnel analyzed through disclosure documents. So, this includes a private placement memorandum.
Avoiding the disclosure requirements of a public offering can mean significant savings.
Firms must still file disclosure forms with the SEC. But, the forms (Form D) only include the names of the company’s principals. So, this is after they close on the sale of their securities.
Negotiating Caveats
These investments come with several stipulations. They carry a high degree of risk for many reasons.
First, private placements happen in the early stages of enterprise development. These are firms that have not been thoroughly tested in the open market.
Second, private placements often come with withholding periods. Investors in these securities cannot sell their shares for at least a year.
Third, because private placements are not publicly traded, they have far less liquidity.
Common stock investors can do open market selling. This is when signs of operational struggles and stock price declines emerge. Private placements may lock investors into a sinking ship.
There are also restrictions on who can invest.
Firms must have assets of at least $5 million. Individual investors must have a net worth of over $1 million. Else their gross income for each of the last two years must be more than $200,000.
So, there must be an expectation of the same income level in the current year.
Differences between the Private Placement Program and Public Offering
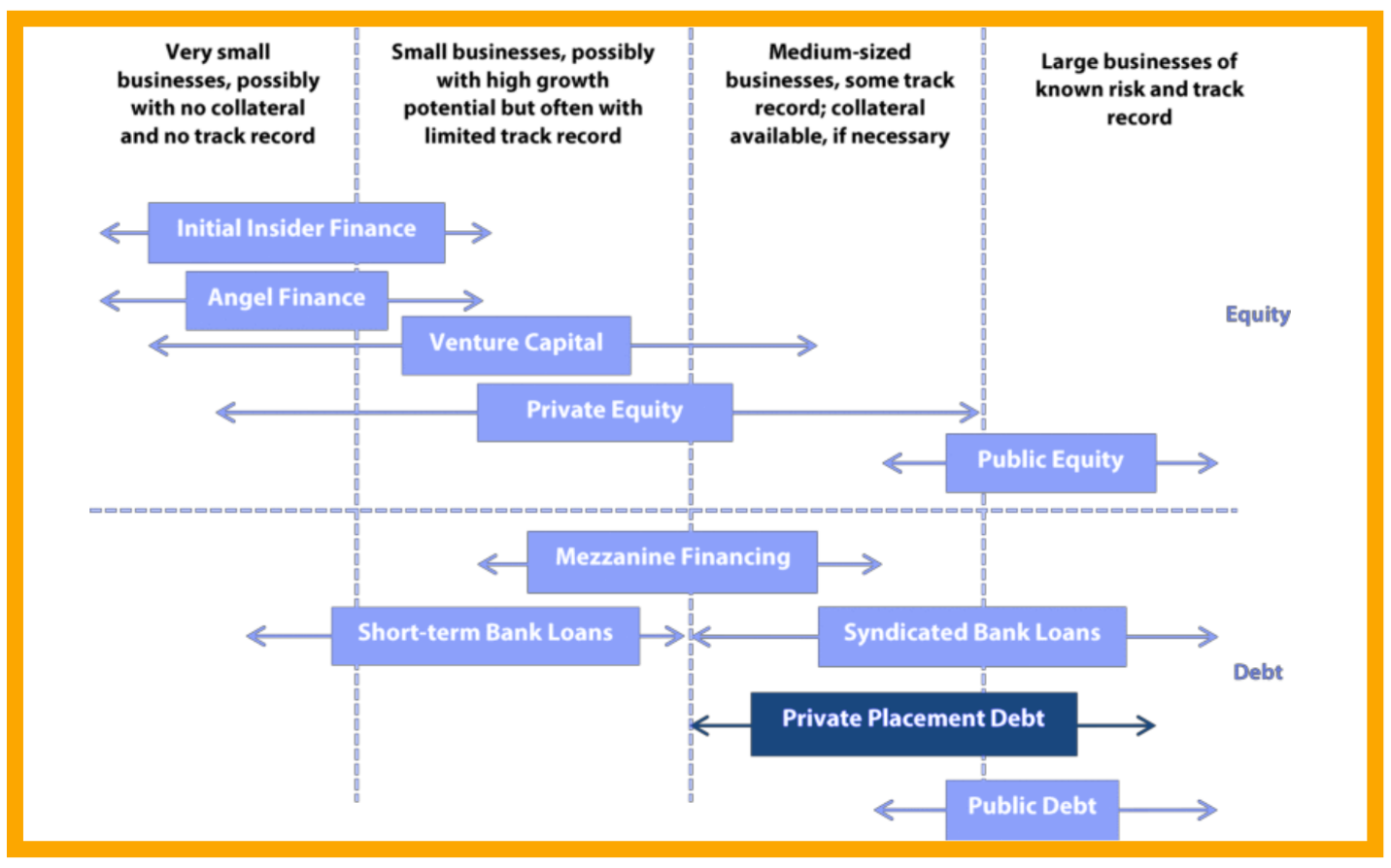
- In private placement, the securities are sold to a group of investors. In contrast, in the public offering, the securities are offered to the public.
- Both public and private companies can issue a private placement of shares. Whereas in a public offering, the company is either listed or listed after the offer is made.
- Private placements may not be required to be registered with a regulator. In contrast, public securities offered have to be registered with a regulator.
Fascinating Facts About the Private Placement Market:
- From 2010 through 2016, $20.2 trillion was raised in total capital. $8.8 trillion was raised through registered securities.
- The majority of $11.38 trillion was raised from exempt offerings, i.e., private placements. This is according to the SEC’s Division of Economic Risk Analysis (DERA).
- Private placements have grown considerably in recent years. It was $1.87 trillion in 2015. It was $1.68 trillion in 2016. In 2014, there were 33,429 Regulation D offerings. This accounted for about $1.3 trillion raised.
- During 2014, Issuers in non-financial industries reported raising $133 billion. (Think actual companies money raising money vs. investment funds raising money)
- Regulation D capital continues to be positively correlated with public market performance. This suggests that capital formation in the unregistered market is pro-cyclical. So, the strength of the unregistered market is closely tied to the public market’s health.
- Consistent with Regulation D’s original intent to target small businesses’ capital formation needs. The offer size median of non-financial issuers is less than $2 million.
- Two hundred sixty thousand investors participated in Regulation D offerings for the period 2009-2016. This is indicated by Aggregated Form D information. Additionally, the SEC believes the number is lower than 260,000.
Rules and Regulations of Private Placements
There are a few conditions to qualify as a private placement. An issuer offering must meet either the requirement of Sections 3(b) or 4(2) of the 1933 Act.
It is as developed through SEC interpretation and court decisions. Else, it must follow the conditions set out under Regulation D of the 1933 Act.
Persons may claim the exemption from the 1933 Act. So, they carry the burden of proving that their activities came within that exemption.
What is Regulation D?
Regulation D is a series of six rules. These are Rules 501-506.
It establishes three transactional exemptions from the registration requirements of the 1933 Act.
A company may meet the requirements. Then they are exempt from having to register the securities they are looking to sell.
What is SEC Form D?
Form D is a document filed with the SEC.
Firms issuing private placements must file it. This must be done within 14 days from the first sales of securities.
Therefore, the issuer’s attorney creates these filings.
What are “Accredited Investors”?
One of the major examples of private placements is referred to as “accredited investors.”
This is outside of massive institutions and funds. A startup may be looking for its first funding. Then they will often approach this group.
So, who are accredited investors? “Accredited Investor” is defined in Rule 501(a).
The categories of accredited investors are as follows:
- General partners, executive officers, and Directors of the issuer. This includes general partners of general partners in two-tier syndicating.
- Buyers whose net worth equals or exceeds $1 million. It is important to note that while there is no definition of “net worth” in regulation D, the value of the purchaser’s home is excluded in Section 501(a)(5)(i)(A)
- Natural person purchasers who have “income” over $200,000 in each of the two most recent years and who reasonably expect an income over $200,000 in the current year (or $300,000, jointly with their spouse).
- An organization generally comes under a single accredited investor. This continues unless it was organized for the specific purpose of acquiring the securities offered. In that case, each beneficial owner of the security is counted separately.
Private Placement Offering Memorandum
An issuer has to meet Regulation D’s requirement or the requirements of Section 4(2) of the 1933 Act.
So, the issuer always makes extensive disclosures. It is regarding the character, nature, and risk factors relating to an offering.
Hence, the disclosure document often is labeled “Offering Memorandum.” An issuer’s attorney creates offering Memorandums.
Conclusion
The volume of private placement issues hit $49.17 billion in 2013. This was off 9.5 percent from 2012’s record levels.
This was the second-highest posting of private placement issuance volume. There are many examples in which private placements attract savvy high net worth investors.
They seek diversification with a range of alternatives. These are only marginally correlated to public markets in the current market environment. They evaluate businesses and invest accordingly.
Firms get robust opportunities to generate capital through private placements. So, it helps them to expand their enterprises without going public.
They offer investors early access to a wide range of promising projects. Hence, it has the potential for steep returns in a lackluster investment landscape.









